Why do abbreviations tend to disrupt MT results? The problem is actually in the standard order of operations, applying supported glossaries after the MT has done its work. At Intento, we’ve crafted a new glossary type specifically for ad hoc abbreviations, adjusting the flow so that all abbreviations are extended before being sent to your MT.
Keep reading to find out how this novel approach will save your next MT project by ensuring all ad-hoc abbreviations are successfully translated within the correct context.
• • •
The MT landscape is continually evolving, putting critics to shame with swift and significant improvements over the last few years. The latest innovation — a glossary type used to facilitate more reliable translations of ad hoc abbreviations — will prove to be a game-changer for those searching for solutions oriented around industry-specific texts, user-generated content, or informal communications.
Many NMT providers support similar glossaries today, but they are typically implemented in the post-editing stage, replacing the MT output with a separate translation. For this strategy to work, the MT needs to know the context of the source word, or the final product will be corrupted, leaving the glossary useless. Take, for example, a hypothetical statement with medical abbreviations: “The pt was given abx”. Unless the MT has been given the information for the meaning of the ad hoc abbreviations, pt (patient) and abx = (antibiotics), the owner of the text is risking the omission of a necessary segment of their communication. Ad hoc abbreviations can also be a nightmare for human translators who need to check each ad hoc abbreviation within an abbreviation list which could span thousands of entries — explaining the low ratings of post-editor productivity in these cases. No matter how you approach each project, introducing the Intento Abbreviation Glossary to your workflow will benefit your translation experience, reducing both the cost and effort put into post-editing by minimizing the risk of manipulated translation outcomes.
• • •
Facilitating a more effective and efficient workflow
Once applied to your Abbreviations Glossary, you can rely on the abbreviated phrase being properly digested whenever it appears in a source text. That’s because, unlike other glossaries, Abbreviations become the first step in the MT process before any translation or fine-tuning has occurred, and it’s as simple as adding any other glossary. To get started, select the Abbreviation Glossary in your workflow, and add a new term by inputting both the abbreviation and its target expanded phrases, as well as a source language for the abbreviations. Keeping with the previous example, you would input ‘pt’ and ‘abx’ as source phrases, with ‘patient’ and ‘antibiotics’ respectively as target texts.
“Take abx as directed on the packet or the pt information leaflet that comes with the medication, or as instructed by your pharmacist”
- We have source phrases in our Abbreviation Glossary, ‘pt’ which is decrypted to read as the target text, ‘patient’, and ‘abx’, decrypted as ‘antibiotics’
- The user begins the text translation (i.e from English to Spanish)
- The sentence “Take abx as directed on the packet or the pt information leaflet that comes with the medication, or as instructed by your pharmacist” is sent through for processing
- In the pre-processing phase, the abbreviated ‘abx’ and ‘pt’ are automatically detected, and replaced with the target texts, ‘antibiotics’ and ‘patient’
- The complete sentence, “Take antibiotics as directed on the packet or the patient information leaflet that comes with the medication, or as instructed by your pharmacist”, is sent to the provider for translation
- The machine translation output reads, “Tome los antibióticos como se indica en el paquete o en el folleto de información para el paciente que viene con el medicamento, o según las instrucciones de su farmacéutico”

Pipeline
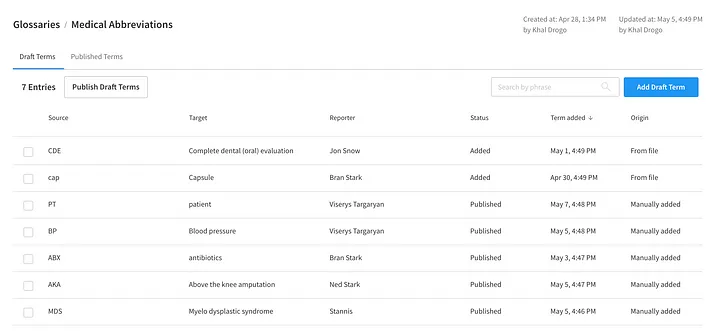
Abbreviations Glossary UI
Replacing the ad hoc abbreviation before the translation process gives your MT provider more context to work with for the translation, which can be the make-it-or-break-it factor in your project — and working in an industry with substantial ad hoc abbreviations will lead you to waste way too much time in your post-editing operations. This isn’t just for industry-specific texts, but applicable to any business operations that require an understanding of ad hoc abbreviations.
As a plus, when used via Intento connectors to CAT/TMS tools, such as SDL Trados, memoQ, XTM, or Memsource, the Abbreviations Glossary approach keeps your Translation Memories in the right shape: where the source segment contains the abbreviations, and the target is a correct translation.
Cases for better translations in e-commerce and customer service
If you work in e-commerce, you’re probably familiar with the importance of training specific acronyms or abbreviations. It is essential not only for the information that you are supplying your customers but also for the user-generated content that is populating your product boards. Advertising a 1st ed novel to your French customer base, you need to know that your output will relay the correct information about your ‘première édition’ without losing the core value of your product.
Extending abbreviation use to customer service as well, imagine receiving a note from a client riddled with the abbreviated language of someone in a hurry: “Afaik, our ppl can’t solve this — will you pls try and lmk soon?”. Trying to clean a sentence like that up in the post-translation phase would simply not work based on the probable level of corruption to the sentence. However, by extending the abbreviations before sending the statement to MT, your provider would simply have to translate, “As far as I know, our people can’t solve this — will you please try and let me know soon”, and the chances of success are exponentially higher.
• • •
Universally beneficial
The abbreviations cause problems not only for machines but for human translators too. Even subject matter experts have to sift through large abbreviation glossaries to make sense of text with ad hoc abbreviations, causing productivity to slip from 300 words per hour to a mere150.
Whether you’re working with industry-specific terminology, user-generated content, or informal conversations, the chances are that your MT efforts can benefit from a better understanding of ad hoc abbreviations. By applying the glossary before in the pre-processing phase, Intento Abbreviations dramatically cuts down the risk of segment distortion, raising post-editing productivity tenfold — from 150 to 1,500 words per hour.
To learn more about how to optimize your MT with Intento Abbreviations Glossaries, please book a demo, and happy translating!



